Elbow Arthritis
Elbow arthritis is a painful condition that affects the elbow. There are a number of different types of arthritis that may affect the elbow such as Osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis or arthritis after fractures.
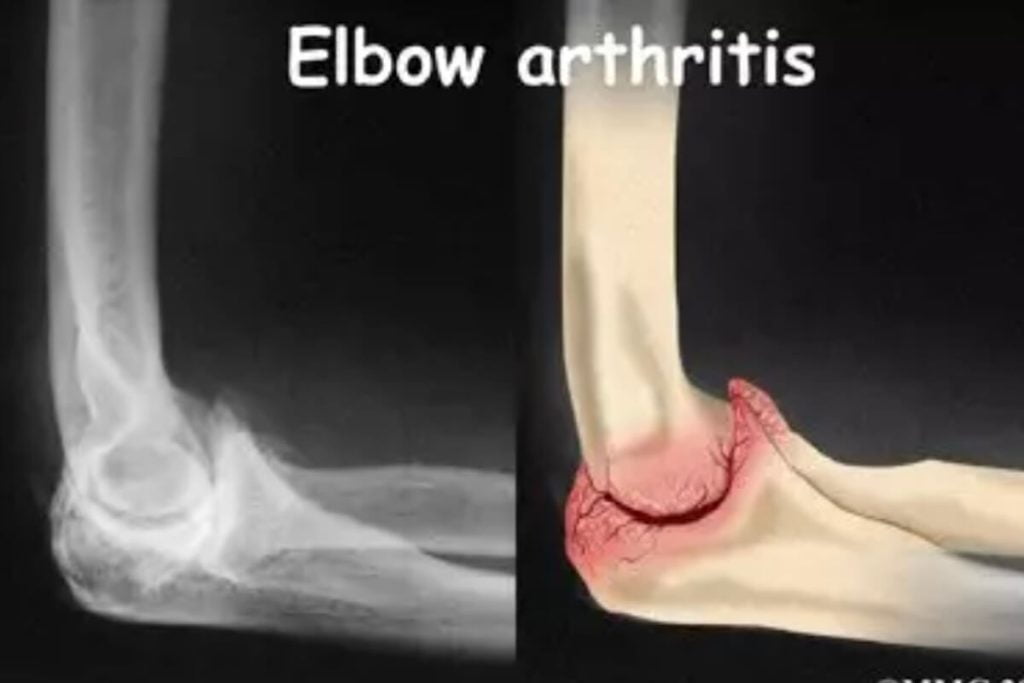
Elbow Arthritis
Elbow arthritis is a condition that affects the joints in the elbow, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. It is a degenerative disease that occurs when the cartilage in the joint wears away, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Elbow arthritis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it difficult to perform daily activities and participate in sports or hobbies.
Causes of Elbow Arthritis
Elbow arthritis can be caused by various factors, including age, injury, and certain medical conditions. The most common type of elbow arthritis is osteoarthritis, which occurs due to the natural wear and tear of the joint over time. As we age, the cartilage in our joints starts to deteriorate, leading to the development of arthritis. Another common cause of elbow arthritis is rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints. Injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, can also contribute to the development of arthritis in the elbow.
Risk Factors for Elbow Arthritis
Certain factors increase the risk of developing elbow arthritis. One of the primary risk factors is age, as the chances of developing arthritis increase as we get older. Other risk factors include a family history of arthritis, previous joint injuries, repetitive stress on the elbow joint (such as in athletes or manual laborers), and certain medical conditions like gout or lupus. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek early treatment if necessary.
Common Symptoms of Elbow Arthritis
The symptoms of elbow arthritis can vary from person to person, but common signs include pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the elbow joint. Individuals with arthritis may experience pain that worsens with movement or activities that put pressure on the joint. The joint may also feel warm to the touch, and there may be a noticeable decrease in grip strength. In some cases, individuals may experience a clicking or grinding sensation in the elbow joint. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of elbow arthritis
To diagnose elbow arthritis, the orthopedist will perform a comprehensive evaluation, which may include a physical exam, medical history review, and imaging tests. During the physical exam, the doctor will assess the range of motion in the elbow joint, look for signs of inflammation, and test grip strength. X-rays or other imaging tests may be ordered to visualize the joint and assess the extent of the damage. Blood tests may also be done to rule out other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment Options for Elbow Arthritis
While there is no cure for elbow arthritis, several treatment options can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition. The treatment approach will depend on the severity of the arthritis and the individual’s specific needs. Common treatment options include medications, physical therapy, surgical intervention, and lifestyle changes.
Medications for Elbow Arthritis
Medications can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with elbow arthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed to manage pain and swelling. Corticosteroid injections may be recommended for individuals with severe pain or inflammation. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to slow down the progression of the disease.
Physical Therapy for Elbow Arthritis
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing elbow arthritis. A physical therapist can design a customized exercise program to improve joint strength and flexibility, reduce pain, and enhance overall function. The therapist may incorporate various techniques, such as manual therapy, stretching exercises, and strengthening exercises, to address the specific needs of the individual.
Surgical Intervention for Elbow Arthritis
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat severe elbow arthritis that does not respond to conservative treatments. The most common surgical procedure for elbow arthritis is arthroscopy, in which a small camera is inserted into the joint to remove damaged tissue or bone spurs. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be recommended, where the damaged joint is replaced with an artificial joint.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Elbow Arthritis
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can help manage elbow arthritis and improve overall joint health. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential to reduce stress on the joints. Regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, can help improve joint flexibility and strengthen the surrounding muscles. It is also important to avoid activities that put excessive strain on the elbow joint and to take regular breaks to rest the joint during repetitive tasks.
Prevention of elbow arthritis
Although some risk factors for elbow arthritis cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to reduce your chances of developing this condition. Protecting your joints from injury by wearing appropriate protective gear during sports or physical activities is important. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help keep joints strong and healthy. If you have a family history of arthritis or other risk factors, it is recommended that you consult your doctor for personalized preventive strategies.
A diagnosis of elbow arthritis is made based on the history of a gradual onset of pain in the elbow. Pain is usually aching in nature and experienced over the front or the back of the elbow. It is often associated with stiffness in the elbow and a feeling of roughness when moving the elbow. Some patients may experience pins and needles in the hand from irritation of the ulnar nerve. Examination shows painful restriction of movements of the elbow. An X-ray may demonstrate narrowing of the joint, erosion and formation of spurs. Special imaging with a CT scan or an MRI scan is sometimes necessary to aid in planning treatment.
In the early phase, pain may be controlled with activity modification and the use of pain relieving or anti-inflammatory medication.
Physiotherapy: You may be advised to see a physiotherapist to treat the stiffness and any associated muscle weakness.
Steroid injection: A steroid injection placed accurately into the joint may provide short-term pain relief. Injections should be avoided if surgery is being contemplated.
Visco-supplement injection: Hyaluronic acid is found in normal joint fluid and helps to lubricate the joint and remove by-products of inflammation. Synthetic hyaluronic acid is available for injection into the joint and may provide substantial relief from pain for a period of 3-6 months in patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. These injections are best performed under image guidance.
Arthroscopic Surgery: If symptoms persist despite adequate nonoperative treatment and if the arthritis is not severe, it may be appropriate to undertake arthroscopic treatment. This consists of “key-hole” surgery to remove loose fragments or bone spurs from the joint and release the tight capsule or sleeve of the joint. It may be necessary to decompress the ulnar nerve. Following surgery symptoms will usually improve over a period of time. For further information on surgical treatment, please refer to the section on “Arthroscopy for Bone spurs and Elbow Arthritis”.
Elbow replacement surgery: If the arthritis is advanced and the pain has failed to respond to other treatment measures, it may be appropriate to consider joint replacement surgery. Elbow replacements are successful at relieving pain and restoring function and quality of life. For further information please refer to the section on “Total elbow replacement”.
