Calcific tendonitis treatment
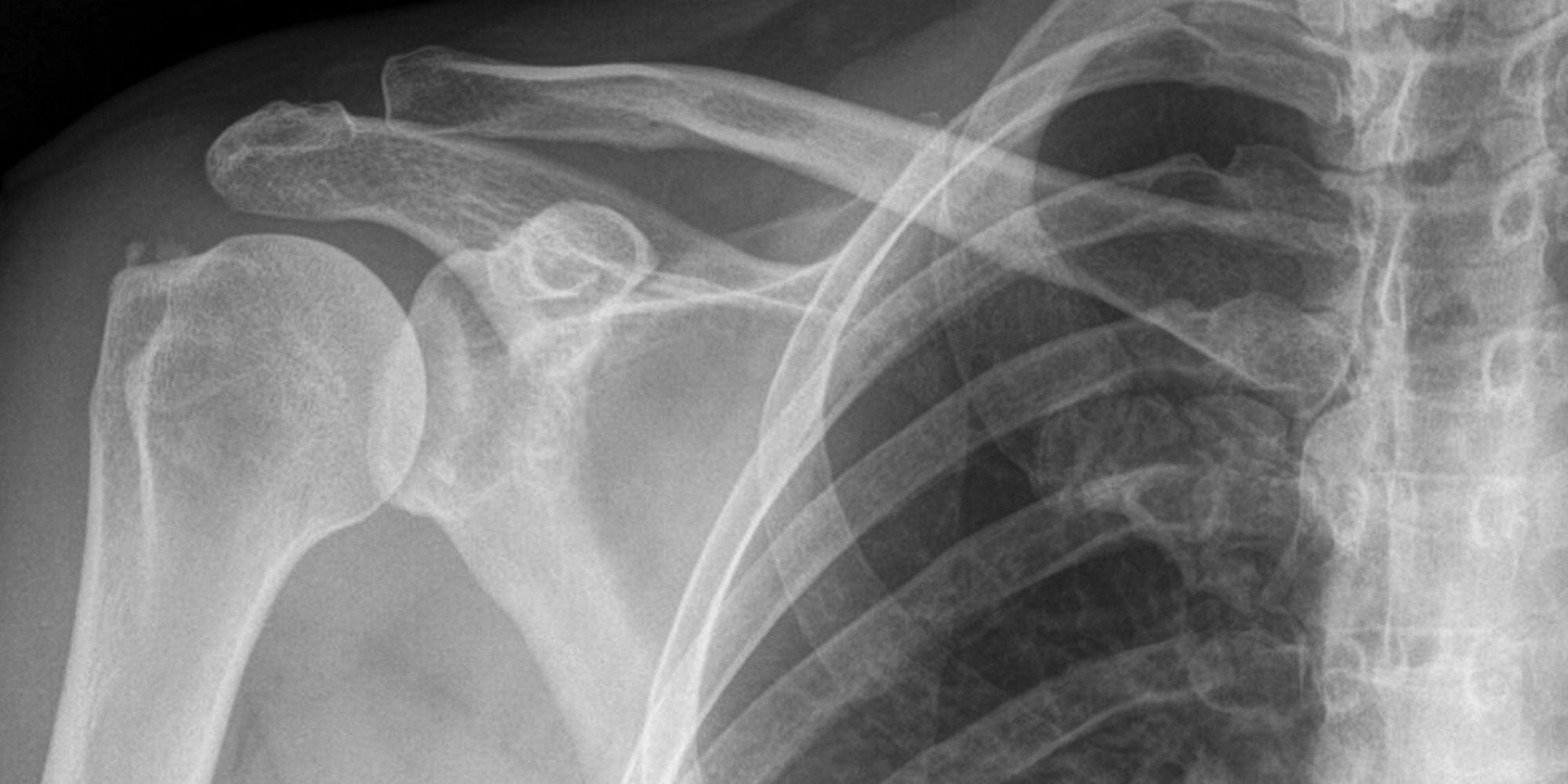
Calcific tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the tendons due to the buildup of calcium deposits. This condition commonly affects the shoulders, but it can also occur in other areas of the body such as the hips, knees, and ankles. If you are experiencing symptoms of calcific tendonitis, it is important to understand the treatment options available to you. In this article, we will explore the various treatment methods for calcific tendonitis and help you find the best option for your specific needs.
Causes and Symptoms of Calcific Tendonitis
Calcific tendonitis is typically caused by repetitive motion or overuse of a specific tendon. The exact cause of the calcium deposits is still unknown, but it is believed to be a result of the body’s attempt to repair micro-tears in the tendon. This leads to the accumulation of calcium over time, causing pain and inflammation.
The most common symptom of calcific tendonitis is a sharp, intense pain in the affected area. This pain is often worse with movement or pressure on the tendon. Other symptoms may include swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.
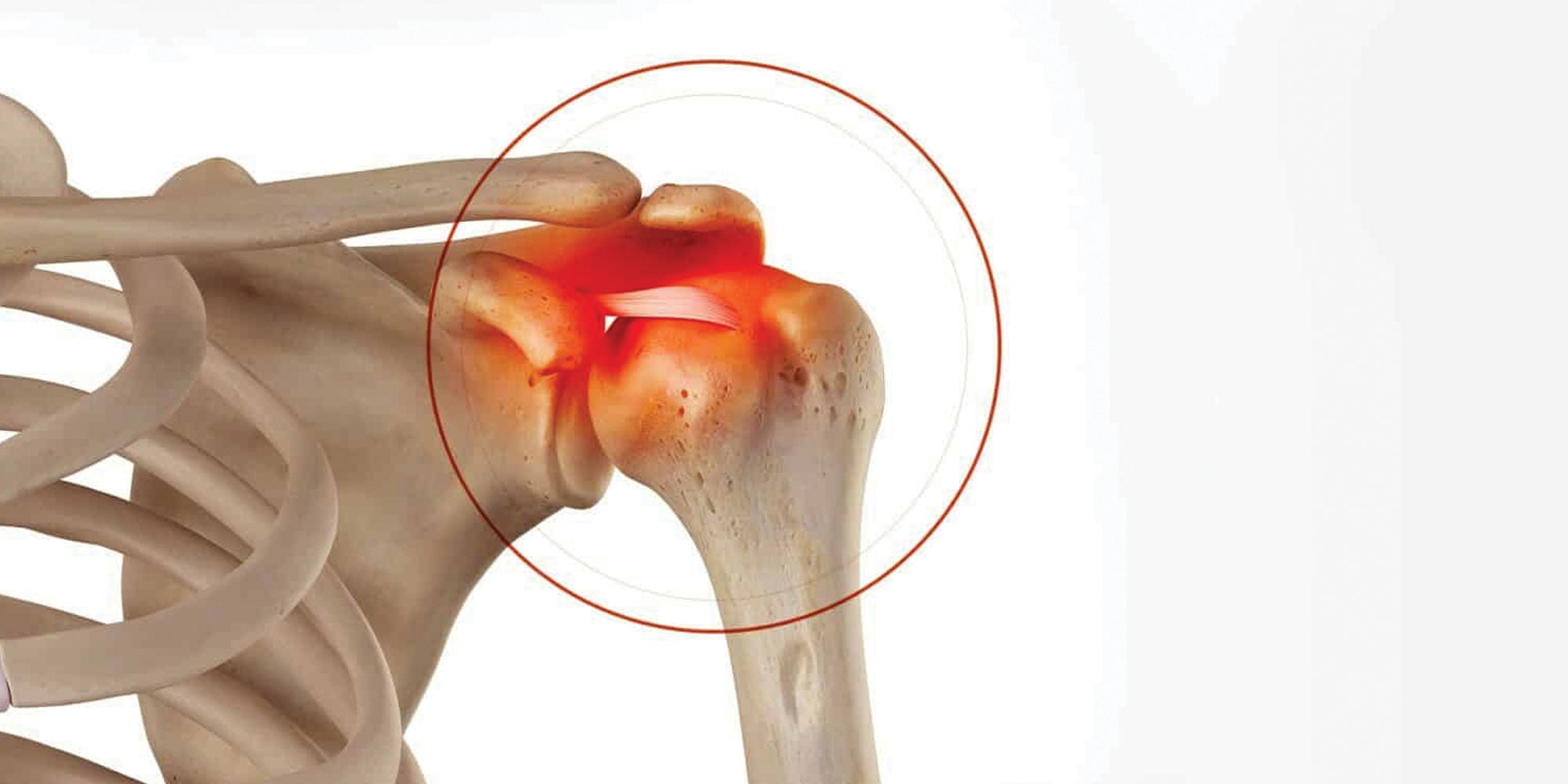
Diagnosing Calcific Tendonitis
To diagnose calcific tendonitis, your doctor will perform a physical examination and review your medical history. They may also order diagnostic imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRI scans to confirm the presence of calcium deposits in the affected tendon.
Once a diagnosis is made, your doctor will work with you to determine the best course of treatment based on the severity of your symptoms and the location of the calcium deposits
Traditional Treatment Options for Calcific Tendonitis
Traditional treatment options for calcific tendonitis include both non-surgical and surgical approaches. Non-surgical treatments are typically attempted first and may include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that worsen the pain can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected tendon, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter or prescription medications can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
If non-surgical treatments do not provide sufficient relief, your doctor may recommend surgical intervention.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Calcific Tendonitis
If non-surgical treatments are ineffective, there are several non-invasive procedures that can be performed to alleviate symptoms of calcific tendonitis:
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT): This treatment involves the use of high-energy shockwaves to break up the calcium deposits and stimulate healing in the affected tendon.
- Ultrasound-Guided Needle Aspiration: In this procedure, a needle is used to remove the calcium deposits from the tendon under ultrasound guidance. This can provide immediate relief of symptoms.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids directly into the affected tendon can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
These non-surgical treatment options are generally less invasive and have shorter recovery times compared to surgical interventions.
Surgical Treatment Options for Calcific Tendonitis
In cases where non-surgical treatments have failed or the calcium deposits are particularly large or problematic, surgical intervention may be necessary. Some surgical treatment options for calcific tendonitis include:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions and using a tiny camera (arthroscope) to visualize and remove the calcium deposits.
- Open Surgery: In more severe cases, open surgery may be required to remove the calcium deposits and repair any damage to the affected tendon.
Surgical treatment options are typically reserved for cases that do not respond to conservative measures and should be discussed thoroughly with your doctor.
Rehabilitation and Recovery After Treatment
After undergoing treatment for calcific tendonitis, rehabilitation and recovery are crucial for restoring function and preventing future recurrence. Physical therapy exercises will be prescribed to help regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected area. It is important to follow the guidance of your healthcare professional and diligently perform the prescribed exercises to optimize your recovery.
The duration of rehabilitation and recovery will vary depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment received. It is essential to be patient and consistent with your rehabilitation program to achieve the best possible outcome
Prevention and Management Strategies for Calcific Tendonitis
While calcific tendonitis cannot always be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and manage the condition:
- Proper Body Mechanics: Practice good posture and body mechanics during activities to minimize stress on the tendons.
- Gradual Progression: Avoid sudden increases in activity or repetitive motions that can strain the tendons. Gradually increase intensity and duration to allow your body to adapt.
- Cross-Training: Engage in a variety of activities to distribute stress evenly across different muscle groups and tendons.
- Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Always warm up before exercise and cool down afterward to prepare your muscles and tendons for activity and promote recovery.
Conclusion: Finding the Best Treatment Option for Calcific Tendonitis
In conclusion, calcific tendonitis can be a painful condition that affects the tendons due to the buildup of calcium deposits. There are various treatment options available, ranging from non-surgical approaches to surgical interventions. Non-surgical treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and medication are typically attempted first, while surgical options may be considered if conservative measures fail.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment option for your specific case. Additionally, rehabilitation and recovery play a crucial role in restoring function and preventing future recurrences. By following proper prevention and management strategies, you can reduce your risk of developing calcific tendonitis and manage the condition effectively.
Remember, if you are experiencing symptoms of calcific tendonitis, seek medical attention promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Don’t let this condition limit your quality of life – take action and find the best treatment option for you.
